Research Group on Visual Computation
- Home
- Projects
- TODER Project
- Demo Software
- Open positions
- COSCH Training School 2015
- Publications
- Intranet
Pose Estimation from Line Correspondences | |
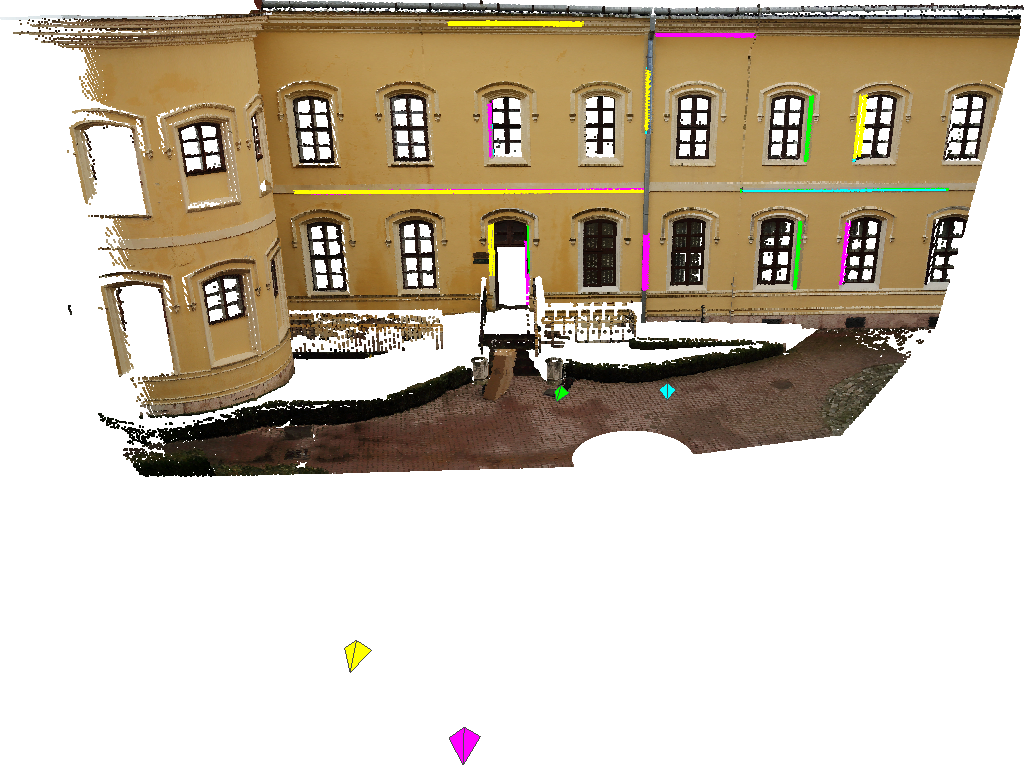 |
|
DescriptionPose estimation is a fundamental building block of various vision applications, e.g. visual odometry, image based localization and navigation, fusion, and augmented reality. Herein, we are interested in absolute pose estimation, which consists of determining the position and orientation of a camera with respect to a 3D world coordinate frame. We propose a novel solution to the gPnL problem with known vertical direction. The vertical direction is typically obtained from an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit). The only assumption about our generalized camera is that projection rays of a 3D line fall into coplanar subsets yielding a pencil of projection planes. Important special cases of such a camera include stereo and multiview perspective camera systems, perspective camera moving along a trajectory, as well as other non-perspective cameras with central omnidirectional or orthographic projection.
For the quantitative evaluation of our generalized pose estimation algorithm with line correspondences, we generated various benchmark datasets of 3D-2D line pairs. Each dataset has 1000 samples. Our method can be used as a least square solver as well as a minimal solver without reformulation. For the minimal case we only need 3 line pairs. The method was quantitatively evaluated on this large synthetic dataset as well as on a real dataset, which confirms its state of the art performance both in terms of quality and computational efficiency. Results
|
- Nora Horanyi, Zoltan Kato, Generalized Pose Estimation from Line Correspondences with Known Vertical Direction, In Proceedings of International Conference on 3D Vision, IEEE, Qingdao, China, pp. 1-10, 2017. [bibtex]
- Nora Horanyi, Zoltan Kato, Multiview Absolute Pose Using 3D - 2D Perspective Line Correspondences and Vertical Direction, In Proceedings of ICCV Workshop on Multiview Relationships in 3D Data, IEEE, Venice, Italy, pp. 1-9, 2017. [bibtex]
Hichem Abdellali has been awarded the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD.) degree...
2022-04-30
Hichem Abdellali has been awarded the KÉPAF Kuba Attila prize...
2021-06-24